ANSI flanges are made to US standards, which use inches. But many projects need metric measurements. This guide gives you the key ANSI flange dimensions in millimeters.
We focus on the most common standard: ASME B16.5. The term “ANSI flange” usually refers to this standard. All dimensions here are converted from the original inch specifications.
Understanding the Key Dimensions
When you work with flanges, you need to know several measurements. Here are the most important ones:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): The name of the flange size, like NPS 2 or NPS 6. It relates to the pipe’s inner diameter.
- Outside Diameter (OD): The total width of the flange face.
- Bolt Circle Diameter (B.C.D.): The diameter of the circle that goes through the center of all bolt holes. This is critical for matching flanges.
- Flange Thickness (T): How thick the flange is.
- Bolt Hole Diameter: The size of the holes for the bolts.
- Number of Bolt Holes: How many bolts are needed.
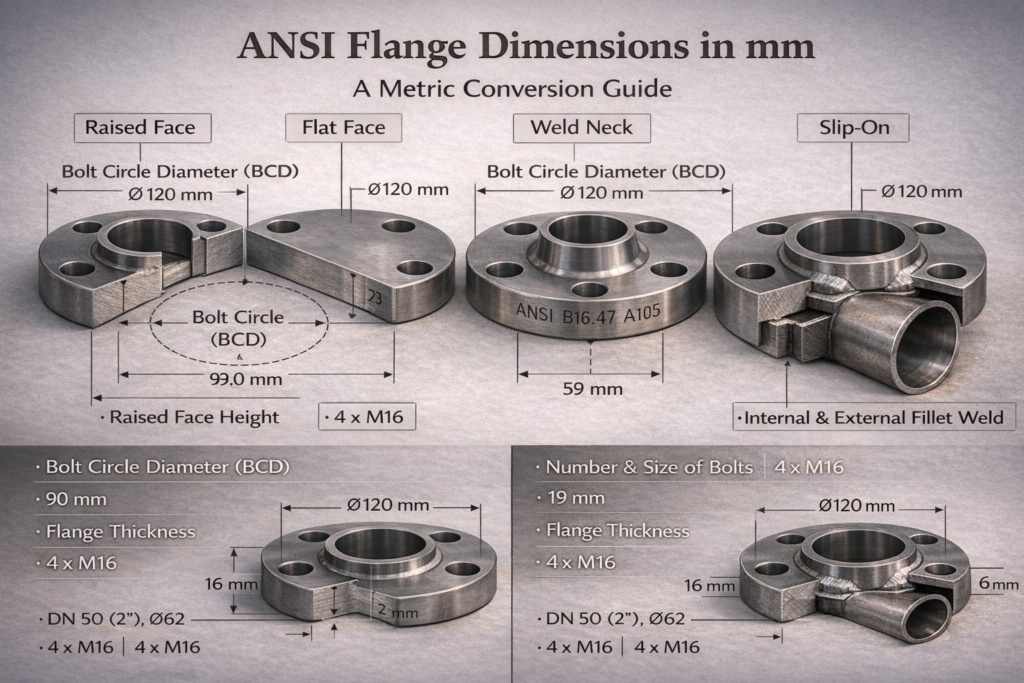
Standard ANSI Flange Dimensions in Millimeters
The tables below show dimensions for common Class 150 and Class 300 flanges. Class 150 is for lower pressure. Class 300 is for higher pressure and is thicker with more bolts.
ANSI/ASME B16.5 Class 150 Flange Dimensions (mm)
| NPS | Outside Diameter (OD) | Flange Thickness (T) | Bolt Circle (B.C.D.) | # of Bolts | Bolt Hole Diameter |
| ½” | 89 mm | 9.7 mm | 60.3 mm | 4 | 15.7 mm |
| 1″ | 108 mm | 12.7 mm | 79.4 mm | 4 | 15.7 mm |
| 2″ | 152 mm | 16.0 mm | 120.7 mm | 4 | 19.1 mm |
| 4″ | 229 mm | 22.4 mm | 190.5 mm | 8 | 19.1 mm |
| 6″ | 279 mm | 24.4 mm | 241.3 mm | 8 | 22.2 mm |
| 8″ | 343 mm | 27.0 mm | 298.5 mm | 8 | 22.2 mm |
| 10″ | 406 mm | 28.4 mm | 362.0 mm | 12 | 25.4 mm |
| 12″ | 483 mm | 30.2 mm | 431.8 mm | 12 | 25.4 mm |
ANSI/ASME B16.5 Class 300 Flange Dimensions (mm)
| NPS | Outside Diameter (OD) | Flange Thickness (T) | Bolt Circle (B.C.D.) | # of Bolts | Bolt Hole Diameter |
| ½” | 95 mm | 14.2 mm | 69.9 mm | 4 | 15.7 mm |
| 1″ | 117 mm | 17.5 mm | 88.9 mm | 4 | 15.7 mm |
| 2″ | 165 mm | 22.4 mm | 127.0 mm | 8 | 19.1 mm |
| 4″ | 254 mm | 25.4 mm | 200.0 mm | 8 | 19.1 mm |
| 6″ | 311 mm | 31.8 mm | 269.9 mm | 12 | 22.2 mm |
| 8″ | 381 mm | 36.6 mm | 330.2 mm | 12 | 22.2 mm |
| 10″ | 445 mm | 39.6 mm | 387.4 mm | 16 | 25.4 mm |
| 12″ | 521 mm | 42.9 mm | 450.8 mm | 16 | 25.4 mm |
Note: The “Raised Face” height is also standardized. For Class 150 and 300 flanges, it is 1.6 mm (1/16 inch).
How to Work with ANSI Flanges in a Metric Project
Using inch-based flanges in a metric system needs some planning.
- Pipe Matching: ANSI flanges connect to pipes measured by “NPS” and “Schedule” (wall thickness). You must find the correct metric pipe with a matching outer diameter (OD). For example, an NPS 2 pipe has an OD of 60.3 mm. You need a pipe with that exact OD.
- Bolt Sizing: Bolts are called “stud bolts.” They are also specified in inches. A ½” bolt has a diameter of about 12.7 mm. You must use bolts with the correct inch diameter and thread (UNC/UNF) to fit the flange holes.
- Tooling: You may need both inch and metric wrenches and calibration tools for installation.
Conversion Formulas and Tolerances
Sometimes you only have inch dimensions. Use these formulas to convert:
- Inches to mm: Multiply the inch value by 25.4.
- Example: A 9-inch Bolt Circle: 9 in * 25.4 = 228.6 mm.
Manufacturing tolerances also exist. For example, the flange thickness for sizes up to 18 inches can have a tolerance of +3.2 mm / -0 mm. The bolt hole spacing tolerance is often ±0.8 mm. This is important for quality checks.
FAQs About ANSI Dimensions in mm
Q: Can I use an ANSI flange with a DIN or EN flange?
A: Usually not. DIN/EN (PN-rated) flanges have completely different dimensions and bolt patterns. They are not directly interchangeable. You need an adapter.
Q: Are these dimensions exact?
A: They are the standard nominal dimensions. Actual manufactured parts will have slight variations within allowed tolerances.
Q: How do I measure an old flange in mm?
A: Use a caliper. Measure the Bolt Circle Diameter (B.C.D.) and the Outside Diameter (OD) in mm. Compare your measurements to the standard tables to identify the flange size and class.
Q: Is the bore size also in inches?
A: Yes. The bore is designed to fit the pipe’s outer diameter (OD), which is based on the inch NPS system. You must match the pipe’s exact OD in mm to the flange’s bore.
Working with ANSI flanges in a metric environment is common. The key is understanding the conversion and knowing that pipe and bolt sizes remain linked to the inch system. Accurate measurement and sourcing are essential for a proper fit.
Need help sourcing ANSI/ASME flanges or matching them to your metric pipework? We supply precision flanges with full dimensional specifications. Provide your project details for a quote here: http://texasflange.com/lp12/